Wathershed, GIS and Graph Theory
Graph theory is a versatile mathematical tool that has found applications across various fields of knowledge. While it's often associated with subjects like organic chemistry—where it helps explore molecular structures—it's also been applied in environmental studies, particularly in conservation efforts. However, the application of graph theory in the environmental sector has mostly been limited to ecological conservation, specifically in studying the connectivity between species and habitats.
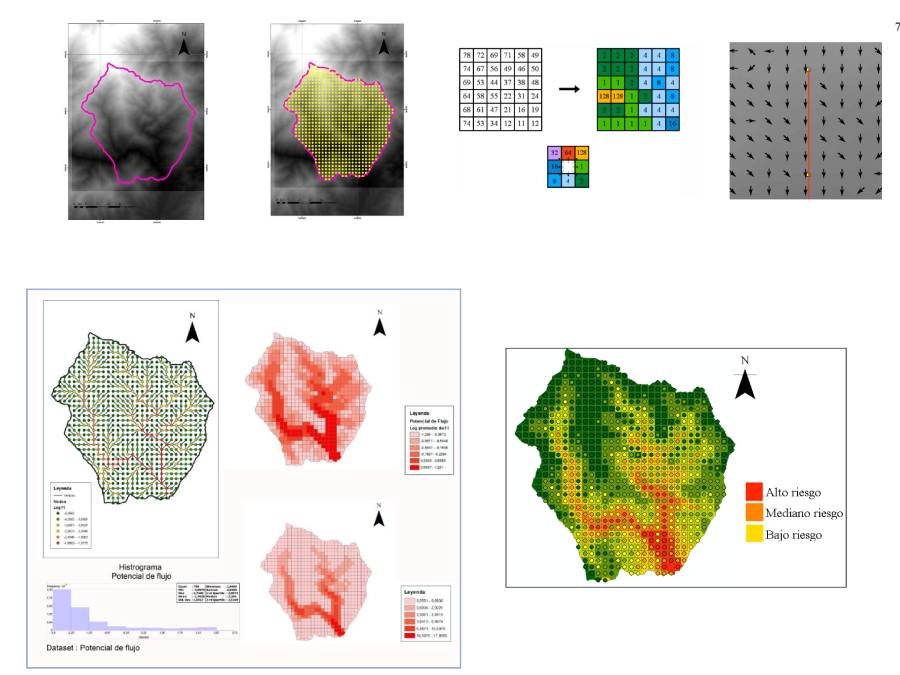
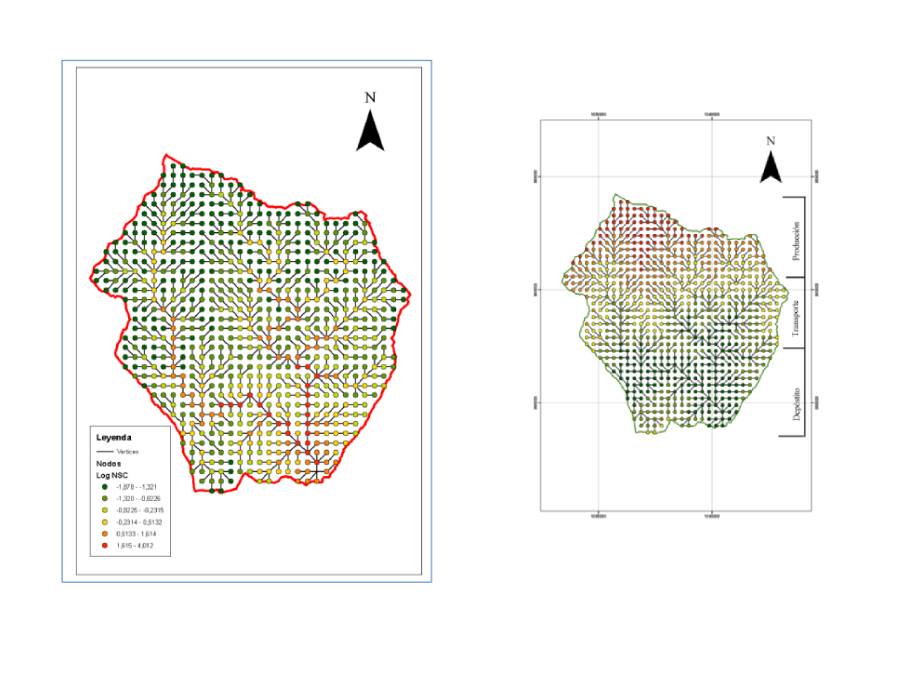
In a broader sense, the environment is a complex tapestry of factors, including social, economic, and ecological dimensions. Recognizing this complexity, Fressard & Cossart (2019) used graph theory in a novel way to examine the sediment transport structures. They developed flow indicators based on hydrological studies, which helped identify areas that are susceptible to erosion processes. This methodology was applied to a specific micro-basin in the Guayuriba river basin, aiming to understand the sediment flow dynamics and provide insights tailored to the region's specific circumstances. Importantly, while the sediment flow data provides a snapshot of reality, the methodology aims to incorporate other variables to reduce uncertainties.